CRISPR gain of function screening
Introduction
This overview is designed to be an introduction to SAM CRISPR gain of function screen at the Target Discovery Institute, Nuffield Department of Medicine, University of Oxford. Below you will find information detailing all aspects of CRISPR screening performed at our facility. The TDI benefits from a broad range of experience across a wide range of screens and our scientists have extensive knowledge of high throughput screening. We are available for consultation at the earliest stages of assay conception and we will work closely with each investigator through all stages of assay development, optimization and screening.
Background
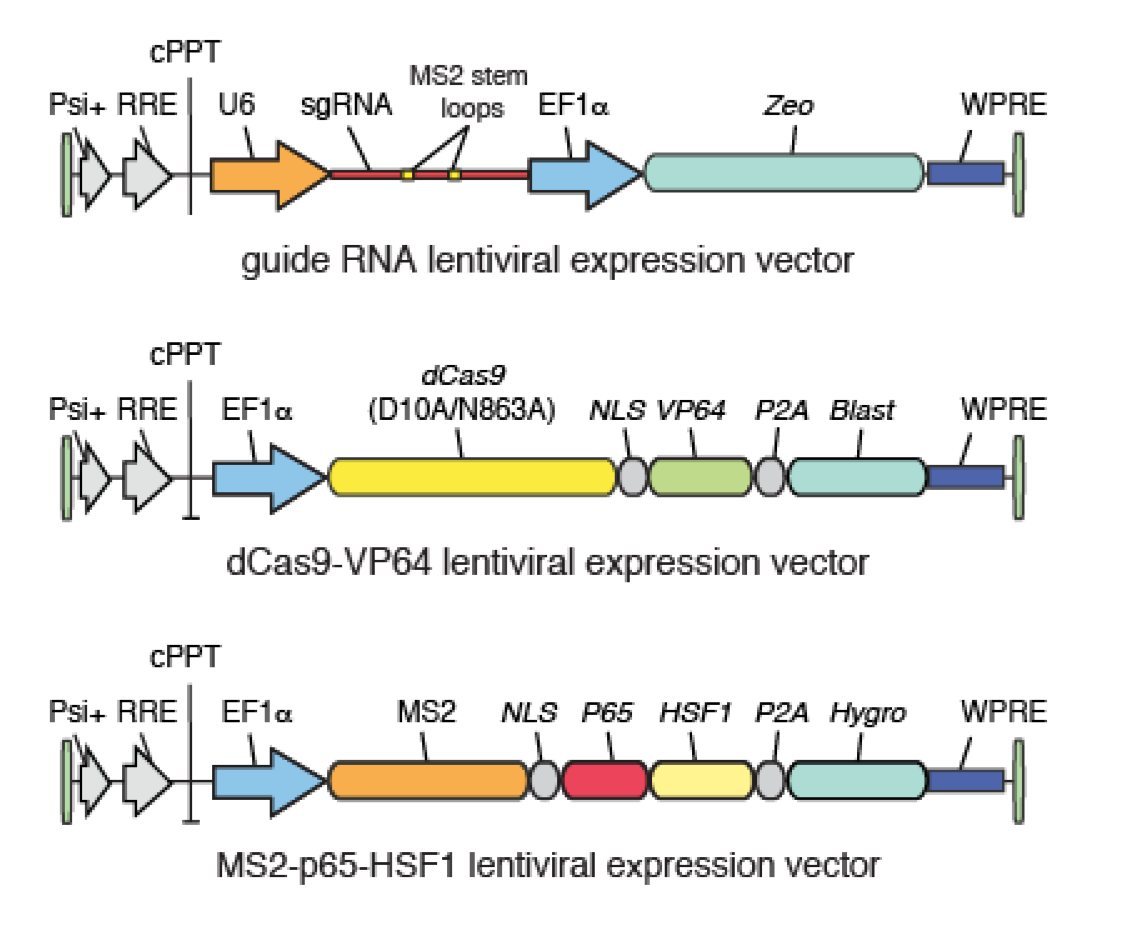
SAM complex consists of three components:
1. A nucleolytically inactive Cas9-VP64 fusion.
2. An sgRNA incorporating two MS2 RNA aptamers at the tetraloop and stem-loop 2.
3. The MS2-P65-HSF1 activation helper protein.
The incorporation of three distinct activation domains - VP64, P65 and HSF1 - into the complex aids robust transcriptional activation through synergy (Figure 1).

SAM can be combined with a human genome-wide sgRNA library to activate all known genes.
LIBRARY DESCRIPTION
For SAM gain-of-function screening, this sgRNA library has to be combined with two additional SAM constructs – dCas9-VP64 and MS2-P65-HSF1 (Addgene). Cells have to be transduced with all three SAM components. To enable co-transduction and selection, all three lentiviral vectors have unique resistance markers (Figure 2).
Optimisation
Several optimisation steps will have to be carried out with cells of choice for optimal screening
- Cell density and Growth kinetics.
- Cell tolerance to Polybrene.
- Kill curve with antibiotics – Blasticidin, Hygromycin, Puromycin and Zeocin.
- Cas9-VP64 and MS2-P65-HSF1 lentivirus functional titre.
- sgRNA lentivirus functional titre to obtain multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 0.3.
Pooled sgRNA lentiviral library is transduced into target cells at MOI of 0.3, which are then selected with puromycin/zeocin, such that each cell receive only one copy of sgRNA, thus knocking out only one target gene per cell. The MOI is the ratio of viral particles to cells and represents the total number of viral particles that are added to a pool of cells. In pooled screening, it is crucially important that each cell in the pool is transduced with only one sgRNA construct to ensure the observed phenotype per cell is the result of one viral particle integration into the cellular DNA. However, by reducing the MOI the number of non-transduced cells increases. Therefore, the MOI has to be carefully decided in advance in order to keep the screen manageable. To avoid multiple integration, we recommend using a low MOI of 0.3-0.5, resulting in 25-39% positive transduced cells (Figure 3).

Screening
For screening, cells will be first transduced with the Cas9-VP64 and MS2-P65-HSF1 lentivirus at MOI of <1 and selected with Hygromycin and Blastcidin for 5-7 days. After complete selection, cells will be transduced with SAM sgRNA library carrying lentiviral vectors at an MOI of 0.3-0.5, and selected with Zeocin for 7 days to obtain a sgRNA coverage of 300-500. Coverage represents the number of cells transduced with a single sgRNA, so coverage of 500 represents 500 cells transduced with a single sgRNA.
Using a library containing 70290 sgRNA and coverage of 500, 35145000 cells will be transduced. In addition, with MOI of 0.3-0.5 with Zeocin selection leading to 75% cell death, up to approximately 141 million cells will be needed for transduction.
For a typical single drug screening at least 36 million cells will be maintained and collected at day 0, for reference, and control arm and drug treated arm. Length of screening will be based on the cell type and treatment. Cells collected will be frozen and used for genomic extraction, PCR and submitted to the Wellcome Trust Centre Human Genetics for NexGen Sequencing (Figure 4). The frequency of guide sequences will be read and targets with a statistically significant difference between conditions and reference control samples will be identified.
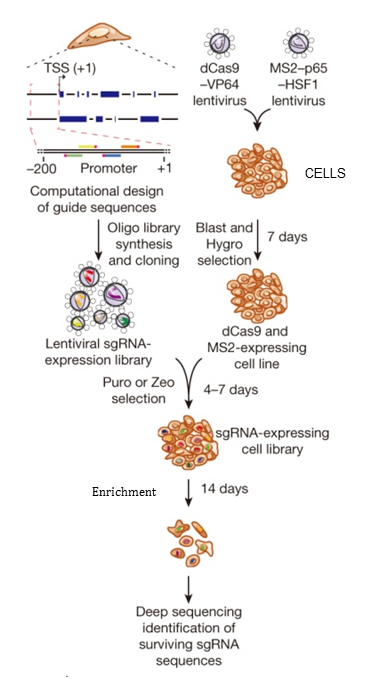
Figure 4. Flow-chart of transcription activation screening using SAM. Blast, blasticidin; Hygro, hygromycin; Puro, puromycin; Zeo, zeocin.
Available Gain of Function library in the TDI
The bellow pooled libraries are avilable as plasmids and Lentivirus in the TDI. Please get in touch with Daniel Ebner for library request, advice or help in screening.
|
Name |
Library Type |
Species |
gRNAs per gene |
Total gRNAs |
|
Activation |
Human |
3 |
70,290 |
|
|
Activation |
Mouse |
3 |
69,716 |
|
|
Activation |
Human |
3 |
70,290 |

